Introduction
Social Movements have consistently transformed societies, driven change, and challenged the status quo. One recurring force behind these collective actions is youth. Across generations and geographies, young people have stood at the forefront of struggles for justice, equality, and freedom. This blog takes a historical perspective on Social Movements, focusing on the vital role that youth have played in shaping their trajectories and outcomes.

What Are Social Movements?
Social Movements are organized efforts by groups of people to achieve specific social or political goals. These movements usually arise in response to perceived injustice, inequality, or unmet needs. They are characterized by collective action, sustained efforts, and the desire to create change at a societal level.
Whether through peaceful protests, cultural revolutions, or political activism, Social Movements have historically altered the course of human development.
The Historical Roots of Social Movements
1. The French Revolution (1789)
One of the earliest large-scale Social Movements, the French Revolution saw a significant youth presence. Young intellectuals and students rallied around ideas of liberty and equality, challenging the monarchy and aristocracy.
2. The Indian Independence Movement (1857–1947)
From Bhagat Singh to Subhas Chandra Bose, youth leaders inspired mass mobilizations against British colonial rule. These young revolutionaries were crucial in energizing the masses and promoting nationalist ideologies.
3. The American Civil Rights Movement (1950s–1960s)
Young people, particularly college students, took center stage in the American Civil Rights Movement. Organizations like SNCC (Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee) led sit-ins, freedom rides, and voter registration drives across the segregated South.

The Power of Youth in Modern Social Movements
4. Anti-Apartheid Movement (South Africa)
Youth were integral in resisting apartheid. The 1976 Soweto Uprising, where thousands of schoolchildren protested against discriminatory education policies, showcased the courage and resilience of South African youth.
5. Tiananmen Square Protests (1989)
Chinese university students led this pro-democracy movement. Though the government’s response was brutal, the movement highlighted the political consciousness and bravery of the youth.
6. Arab Spring (2010–2012)
Fueled by social media and youthful energy, this series of protests across the Middle East and North Africa demonstrated how connected and informed youth can transform nations.
7. Fridays for Future (2018–present)
Started by Greta Thunberg, this climate change movement has galvanized millions of young people around the world. Their demand is clear: act now to save the planet.
Characteristics of Youth in Social Movements
- Energetic: Youth bring physical stamina and mental resilience.
- Innovative: They often employ creative strategies, especially through digital platforms.
- Uncompromising: Their idealism drives them to pursue justice relentlessly.
- Risk-takers: Without major family or financial responsibilities, youth often take bold actions.

Technology and Social Movements: A Youth Advantage
Today’s youth have grown up with smartphones, the internet, and social media. These tools have enabled real-time communication, grassroots organizing, and global solidarity. From Twitter hashtags to viral videos, the digital generation amplifies Social Movements in unprecedented ways.
The Challenges Faced by Youth in Social Movements
- Suppression: Governments often target youth leaders for arrests or censorship.
- Marginalization: Older generations sometimes dismiss young voices as naïve.
- Burnout: Continuous activism can lead to emotional and mental fatigue.
- Lack of Resources: Funding and institutional support are often limited.
Despite these obstacles, youth continue to participate in and often lead Social Movements, turning limitations into fuel for innovation and persistence.
Impact of Youth-Led Social Movements
Policy Reforms
Many youth-led Social Movements have directly influenced legislative changes. From civil rights laws to climate policies, governments have had to respond to sustained youth pressure.
Cultural Shifts
Youth movements have changed societal norms around race, gender, sexuality, and the environment. These shifts are often more enduring than policy changes.
Global Solidarity
Youth connect across borders to support global causes. Movements like Black Lives Matter have seen international support from young activists.

Conclusion
Throughout history, Social Movements have been engines of transformation, and youth have been their beating heart. From toppling dictatorships to redefining gender norms, young people have made indelible marks on the fabric of society. Their willingness to question, challenge, and create makes them irreplaceable in the fight for a better world.
The involvement of youth ensures that Social Movements remain dynamic, resilient, and forward-looking. As we face the complex challenges of today — climate change, social inequality, digital privacy — the role of youth will only grow more critical. Empowering and listening to them is not a choice but a necessity.
To ignore the youth in Social Movements is to ignore the future.
FAQs: Understanding Youth’s Role in Social Movements
1. What is the definition of Social Movements?
Social Movements are organized efforts by a group of people to bring about social or political change.
2. Why are youth important in Social Movements?
Youth bring energy, innovation, and courage, making them powerful agents of change.
3. How do Social Movements differ from protests?
Protests are often single events; Social Movements are sustained efforts aimed at long-term change.
4. Can students lead Social Movements?
Yes, students have historically led major movements, including Civil Rights and anti-war protests.
5. Do Social Movements always result in change?
Not always immediately, but they often initiate critical conversations and long-term shifts.
6. How do youth use social media in Social Movements?
They organize, share information, and build global communities using digital platforms.
7. What risks do youth face in activism?
Risks include arrests, violence, online harassment, and academic or professional setbacks.
8. Are youth-led Social Movements more successful?
While success varies, youth movements often gain rapid momentum due to innovation and networking.
9. What role does education play in activism?
Education empowers youth with the knowledge and tools needed for effective activism.
10. How can youth start their own Social Movements?
Identify a cause, build a team, use digital tools, stay informed, and remain committed.

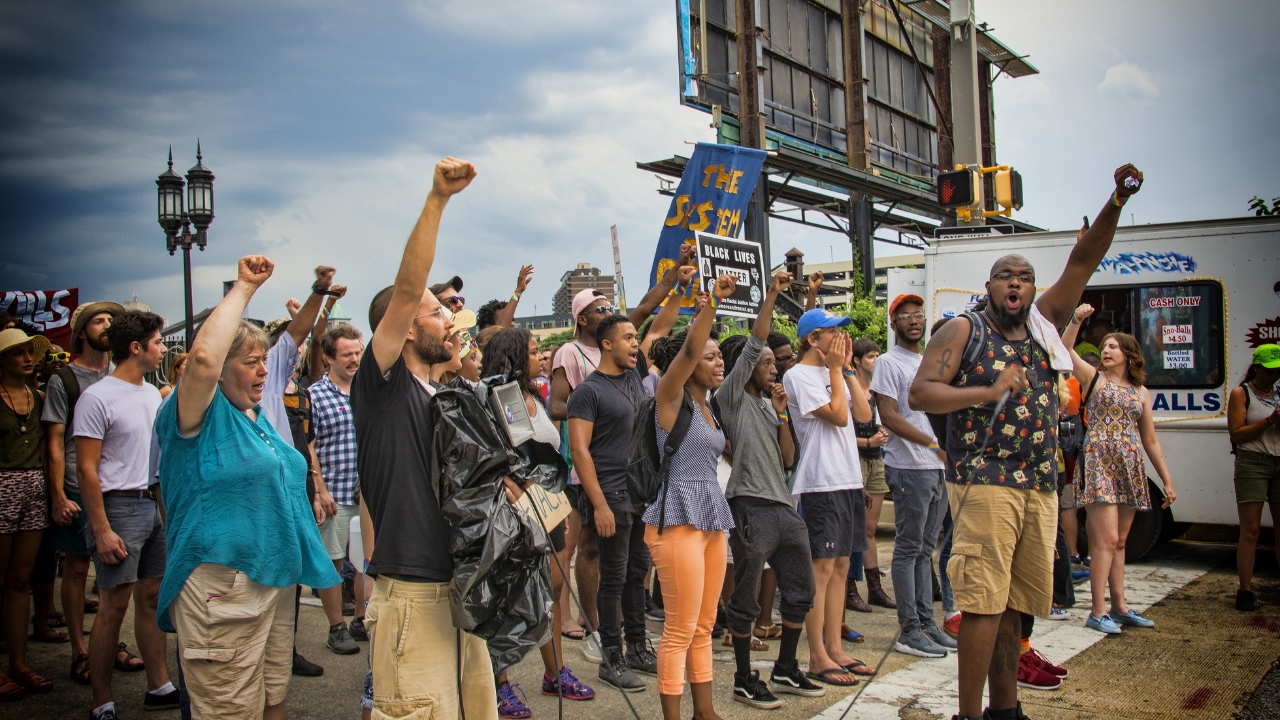
Leave a Reply